Analytical chemistry consist of qualitative as well as quantitative chemical analysis. In a sample, the component to be analysed is called as 'Analyte'. Quantitative chemical analysis consists of two steps:
1. Separation and preconcentration of the analyte.
2. Analysis of the sample.
Separation techniques used are of different types depending on the nature of analyte. Difference in some of the property on the components in a mixture is used as a basis for separation of the components. This property may be difference in size that is used in sieving fine material to separate it from coarse 1 hour may be separation by distillation based on difference in boiling points of the two liquids in a mixture. Various separation techniques like sublimation ,crystallization, etc are used frequently in Chemistry laboratory.
Chromatography is one of such methods used frequently in analytical chemistry. The word chromatography is derived from Greek words meaning "colour" (Chroma) and "write"(Graphy). This technique was first used by Russian botanist M.Tswett in 1906 for separation of coloured plant pigments on column of alumina.
Chromatography is defined as "physical method of separation, in which the components are separated by distribution between two phases". The phase that has large surface area and remains steady is called as 'Stationary Phase' while the other moves through the stationary phase called as 'Mobile phase'.Mixture of various component is equilibrated between two phases. Separation of these components takes place either by the mechanism of 'adsorption' or 'partition'.
Principle
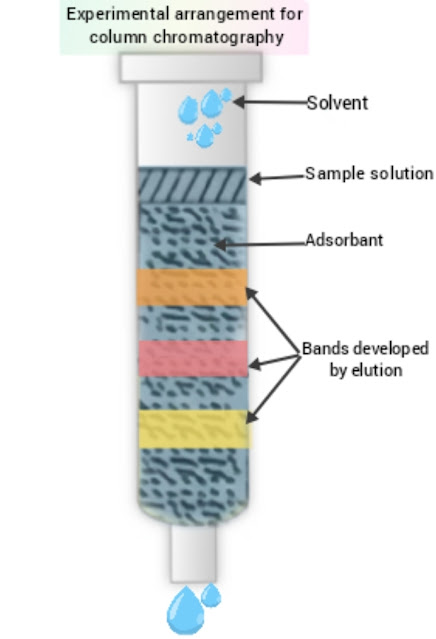
This is a type of adsorption chromatography. Here, the stationary phase is solid while mobile phase is liquid moving over the solid material. Mixture of various components is allowed to flow through a column packed with adsorbent. Different components get adsorbed to different extent and thus get separated from each other. Difference in rates of adsorption of the components act as a basis of separation of these components. As the separation is carried out in a column, it is named as column chromatography.
Technique
In this method, the mixture to be separated is dissolved in a suitable solvent and allowed to pass through a column containing adsorbent. Generally, powdered alumina or silica are used as adsorbents while organic solvent like petroleum ether , cyclohexane etc are used for preparing solution.
The component which has greater adsorbing power is adsorbed in the upper part of the column. The next component is adsorbed in the lower portion. This process continues and different components get adsorbed in different parts of the column. Suitable solvent is added from the top of the column in order to carry out separation and collection of the components. This Liquid added from top of the column is called as eluent. The Liquid emerging out of the column is called as eluate. Different components from different bands in the column. Such column is called as chromatogram.
After development of chromatogram, two procedures can be adopted-
The column may be cut into different parts according to different bands and then each component is extracted using suitable solvent.
The solvent may be added top to take the components one by one out of the column from bottom.
Experimental arrangement is shown in Fig.
Applications
1. In separation of natural products: Naturally occurring organic compounds are called as natural products. They exist in the form of mixtures. Separation of these mixtures is difficult as most of their properties are similar with slight structural variation. Separation of such products is possible using column chromatography.
e.g. Naturally occurring steroids have been separated using column chromatographic technique. Also, constituents of various medicinal plants have been separated using column chromatography.
2. In separation of geometrical isomers:
Cis and trans isomers differ in only relative arrangement of the groups across double bond. The isomers whose functional groups can approach adsorption site more easily get adsorbed strongly compared to the other isomer. Thus separation of these isomers is possible using column chromatography.
e.g. Cis and trans isomers of carboxylic acids have been separated on silica gel column.
3. Separation of diastereomers:
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other are called as diastereomers. They can be separated due to difference in position of various groups in space. Now a days, various adsorbents are available for their quantitative separation.
e.g. separation of distereomeric 7-chloro-7- azobicyclo- heptane has been done on silica gel using pentane dimethyl ether as a solvent.
4. Separation of tautomeric mixture: Keto and enol forms of various organic compounds can be separated using column chromatography.
e.g. Keto and enol forms of p-hydroxylphenyl pyruvic acid and indolyl pyruvic acid have been separated when enol form elutes first and keto form appears later.
5. Separation of racemates:
First successful separation of racemates has been reported using column chromatography technique.
e.g. Enantiomers of Troger's base have been separated using column chromatography.











0 comments:
Post a Comment